rm -fr /home/name/.local/share/Trash/info/*
rm -fr /home/name/.local/share/Trash/files/*
rm -fr /home/name/.local/share/Trash/info/*
rm -fr /home/name/.local/share/Trash/files/*
“Backup” the old Firefox launcher:sudo mv /usr/bin/firefox /usr/bin/firefox-oldCreate a symbolic link pointing to the new Firefox version:sudo ln -s /opt/firefox25/firefox /usr/bin/firefoxNo need to update your icons/shortcuts, they should now launch the new version of Firefox.Your old Firefox version is still installed. If you want to use it, run firefox-old in a terminal or create shortcuts/icons referring to firefox-old. |
| Create a symbolic link pointing to the new Firefox version: sudo ln -s /opt/firefox25/firefox /usr/bin/firefox254 Launch the newly installed Firefox by running firefox25 in a terminal, or create shortcuts/icons referring to firefox25. |
wordpress subfolder:wordpress subfolder:# yum -y update # yum install -y make wget openssl-devel ncurses-devel newt-devel libxml2-devel kernel-devel gcc gcc-c++ sqlite-develTurn Off SELinux by changing the line “enforcing” to “disabled” in /etc/selinux/config file.
SELINUX=disabledOnce you disabled SELinux, you need to reboot the system.
reboot
# su root # apt-get update && apt-get upgrade -y && reboot # apt-get install build-essential wget libssl-dev libncurses5-dev libnewt-dev libxml2-dev linux-headers-$(uname -r) libsqlite3-dev
# cd /usr/src/ # wget http://downloads.asterisk.org/pub/telephony/libpri/libpri-1.4-current.tar.gz # wget http://downloads.asterisk.org/pub/telephony/dahdi-linux-complete/dahdi-linux-complete-current.tar.gz # wget http://downloads.asterisk.org/pub/telephony/asterisk/asterisk-11-current.tar.gzNext, extract the files from source tarballs using “tar command” as shown below.
# tar zxvf dahdi-linux-complete-current.tar.gz # tar zxvf libpri-1.4-current.tar.gz # tar zxvf asterisk-11-current.tar.gz
# cd /usr/src/dahdi-linux-complete-2.6.2+2.6.2/ # make && make install && make config
# cd /usr/src/libpri-1.4.14/ # make && make install
# cd /usr/src/asterisk-11.3.0/ # ./configure && make menuselect && make && make install && make samples && make configRun this command if you’re installing Asterisk on a 64-bit OS.
# cd /usr/src/asterisk-11.3.0/ # ./configure --libdir=/usr/lib64 && make menuselect && make && make install && make samples && make configFollowing are the some Asterisk configuration files and their locations.
# chkconfig dahdi on # chkconfig asterisk onStart the DAHDI and Asterisk.
# service dahdi start # service asterisk start
# asterisk -rvvvvv Asterisk 11.3.0, Copyright (C) 1999 - 2012 Digium, Inc. and others. Created by Mark Spencer <markster@digium.com> Asterisk comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY; type 'core show warranty' for details. This is free software, with components licensed under the GNU General Public License version 2 and other licenses; you are welcome to redistribute it under certain conditions. Type 'core show license' for details. ========================================================================= Connected to Asterisk 11.3.0 currently running on tecmint (pid = 1820) tecmint*CLI>
tecmint*CLI> ! acl ael agent agi aoc calendar cc cdr cel channel cli confbridge config console core data database devstate dialplan dnsmgr dundi event fax features file group hangup help http iax2 indication local logger manager mgcp minivm mixmonitor module moh no originate parkedcalls phoneprov presencestate pri queue realtime reload rtcp rtp say sip skinny stun timing udptl ulimit unistim voicemail
-h : Help. Run '/sbin/asterisk -h' to get a list of the available command line parameters. -C <configfile>: Starts Asterisk with a different configuration file than the default /etc/asterisk/asterisk.conf. -f : Foreground. Starts Asterisk but does not fork as a background daemon. -c : Enables console mode. Starts Asterisk in the foreground (implies -f), with a console command line interface (CLI) that can be used to issue commands and view the state of the system. -r : Remote console. Starts a CLI console which connects to an instance of Asterisk already running on this machine as a background daemon. -R : Remote console. Starts a CLI console which connects to an instance of Asterisk already running on this machine as a background daemon and attempts to reconnect if disconnected. -t : Record soundfiles in /var/tmp and move them where they belong after they are done. -T : Display the time in "Mmm dd hh:mm:ss" format for each line of output to the CLI. -n : Disable console colorization (for use with -c or -r) -i: Prompt for cryptographic initialization passcodes at startup. -p : Run as pseudo-realtime thread. Run with a real-time priority. (Whatever that means.) -q : Quiet mode (supress output) -v : Increase verbosity (multiple v's = more verbose) -V : Display version number and exit. -d : Enable extra debugging across all modules. -g : Makes Asterisk dump core in the case of a segmentation violation. -G <group> : Run as a group other than the caller. -U <user> : Run as a user other than the caller -x <cmd> : Execute command <cmd> (only valid with -r)
[root@gembul ~]# cd /usr/src/
[root@gembul src]# svn checkout http://svn.digium.com/svn/asterisk-gui/trunk asterisk-gui
[root@gembul asterisk-gui]# ./configure
checking build system type... x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu
checking host system type... x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu
checking for uname... /bin/uname
checking for gcc... gcc
##################################### skipped #####################################
configure: Package configured for:
configure: OS type : linux-gnu
configure: Host CPU : x86_64[root@gembul asterisk-gui]# make && make install
##################################### skipped #####################################
+------- Asterisk-GUI Build Complete -------+
+ Asterisk-GUI has successfully been built, +
+ and can be installed by running: +
+ +
+ make install +
+-------------------------------------------+
+---- Asterisk GUI Installation Complete ---+
+ +
+ YOU MUST READ THE SECURITY DOCUMENT +
+ +
+ Asterisk-GUI has successfully been +
+ installed. +
+ +
+-------------------------------------------+
+ +
+ BEFORE THE GUI WILL WORK +
+ +
+ Before the GUI will run, you must perform +
+ some modifications to the Asterisk +
+ configuration files in accordance with +
+ the README file. When done, you can +
+ check your changes by doing: +
+ +
+ make checkconfig +
+ +
+-------------------------------------------+[root@gembul asterisk]# cp -r /etc/asterisk /etc/asterisk.backup
[root@gembul asterisk]# vi /etc/asterisk/manager.conf [general]
enabled = yes
webenabled = yes
port = 5038
bindaddr = 0.0.0.0[root@gembul asterisk]# vi /etc/asterisk/http.conf [general]
enabled = yes
bindaddr = 0.0.0.0
bindport = 8088
prefix = gui
enablestatic = yes[root@gembul asterisk]# asterisk -rAsterisk 1.6.2.21, Copyright (C) 1999 - 2010 Digium, Inc. and others.
Created by Mark Spencer
Asterisk comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY; type 'core show warranty' for details.
This is free software, with components licensed under the GNU General Public
License version 2 and other licenses; you are welcome to redistribute it under
certain conditions. Type 'core show license' for details.
=========================================================================
Connected to Asterisk 1.6.2.21 currently running on gembul (pid = 3108)
Verbosity is at least 3
gembul*CLI> [root@gembul asterisk]# /etc/init.d/asterisk restart
Stopping safe_asterisk: [ OK ]
Shutting down asterisk: [ OK ]
Starting asterisk: [ OK ]
[root@gembul asterisk]# http://localhost:8088/gui/static/config/index.html 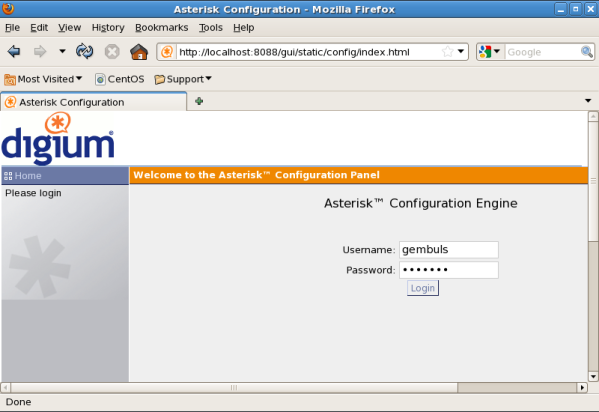
source:
asterisk.org
sourceforge.netnyolong seko : http://gembuls.wordpress.com/2011/12/28/how-to-install-asterisk-gui/












# service mysqld stop
# mkdir /srv/mysql/
# chown mysql:mysql /srv/mysql
# mv /var/lib/mysql/* /srv/mysql/
# nano /etc/mysql/my.cnfChange
datadir=/var/lib/mysqlto
datadir=/srv/mysqland
socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sockto
socket=/srv/mysql/mysql.sockand save the file.
# getenforceRun the semanage command to add a context mapping for /srv/mysql.
# semanage fcontext -a -t mysqld_db_t "/srv/mysql(/.*)?"Now use the restorecon command to apply this context mapping to the running system.
# restorecon -Rv /srv/mysql
# service mysqld start
$ mysql -u root -p
mysql> show databases;If this is working, you’re up and running. Should you get a message that says
ERROR 2002 (HY000): Can’t connect to local MySQL server through socket ‘/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock’then add the following to your /etc/my.cnf
[client] socket = /srv/mysql/mysql.sockOptionally you can just use
$ mysql -u root -p --protocol tcpto avoid connecting via the socket.
sudo yum update -y
sudo yum install httpd -y
sudo yum install php-mysql php php-xml php-mcrypt php-mbstring php-cli php-gd mysql -y
sudo yum install mysql-server -y
sudo yum install openssh-clients -y
sudo yum install wget -y
wget http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
wget http://rpms.famillecollet.com/enterprise/remi-release-6.rpm
sudo rpm -Uvh remi-release-6*.rpm epel-release-6*.rpm
# Once installed you should see some additional repo definitions under the /etc/yum.repos.d directory. #
ls -1 /etc/yum.repos.d/epel* /etc/yum.repos.d/remi.repo
# You should see:
/etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/epel-testing.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/remi.repo
# Enable the remi repository #
sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/remi.repo
# Edit the [remi] portion of the file so that the enabled option is set to 1. This will enable the remi repository.#
name=Les RPM de remi pour Enterprise Linux $releasever - $basearch #baseurl=http://rpms.famillecollet.com/enterprise/$releasever/remi/$basearch/ mirrorlist=http://rpms.famillecollet.com/enterprise/$releasever/remi/mirror enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-remi failovermethod=priority
# Install mcrypt #
sudo yum -y install php-mcrypt
# Add username and password for phpmyadmin #
sudo adduser phpmyadmin sudo passwd phpmyadmin
# Allowing HTTP and HTTPS through the firewall #
sudo vi /etc/sysconfig/iptablesThen add these two lines after the entry allowing port 22:
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 443 -j ACCEPTThen run:
sudo service iptables restart
# adjusting apache config #
sudo vi /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
# Scroll all the way down the the bottom of the Config file by pressing G (Shift + g) then press “a” so you can start manipulating the file.
DocumentRoot /var/www/html ServerName 1.2.3.4# Sroll up until you find #
DirectoryIndex index.html index.php index.sh default.jsp
/var/etc/html
sudo service mysqld start /usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation
cd /var/www/html sudo wget http://sourceforge.net/projects/phpmyadmin/files/phpMyAdmin/3.3.9.1/phpMyAdmin-3.3.9.1-all-languages.tar.gz tar -xzvf phpMyAdmin-3.3.9.1-all-languages.tar.gz -C /var/www/html sudo mv phpMyAdmin-3.3.9.1-all-languages phpmyadmin sudo rm -rf phpMyAdmin-3.3.9.1-all-languages.tar.gz cd /var/www/html sudo chown phpmyadmin.apache phpmyadmin/ cd /var/www/html/phpmyadmin/ sudo mkdir config sudo chmod o+rw config sudo cp config.sample.inc.php config/config.inc.php sudo chmod o+w config/config.inc.php sudo service httpd restart
sudo vi /var/www/html/phpmyadmin/config/config.inc.php
$cfg['blowfish_secret'] = ''; /* YOU MUST FILL IN THIS FOR COOKIE AUTH! */
cd /var/www/html/phpmyadmin/config sudo cp config.inc.php .. cd .. sudo rm -rf config
# Then download create_tables.sql
mysqldump -u username -password databasename > dump.txt mysql -u username -password databasename < dump.txt
sudo yum install ntp -y sudo /sbin/chkconfig ntpd on sudo /etc/init.d/ntpd startIf you want to be able to send email from your contact forms please make sure that you are allowed through your firewall and it helps if you are on a static IP address:
setsebool -P httpd_can_sendmail 1Please leave a comment if this article has helped you! Thanks and enjoy!
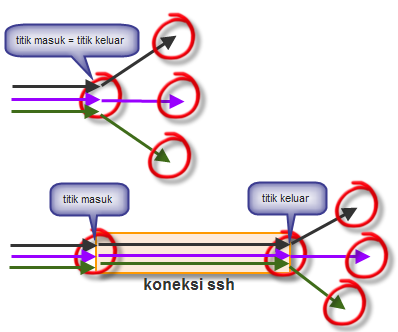
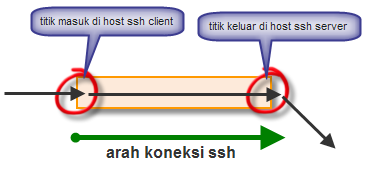
 Jadi
yang perlu diingat dalam perbedaan antara local dan remote port
forwarding adalah posisi titik masuk koneksi yang akan diforward. Bila
titik masuknya ada di komputer yang berperan sebagai ssh client, maka
itu adalah local port forwarding, namun bila titik masuknya di komputer
ssh server, maka itu adalah remote port forwarding.
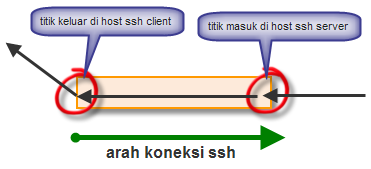
Jadi
yang perlu diingat dalam perbedaan antara local dan remote port
forwarding adalah posisi titik masuk koneksi yang akan diforward. Bila
titik masuknya ada di komputer yang berperan sebagai ssh client, maka
itu adalah local port forwarding, namun bila titik masuknya di komputer
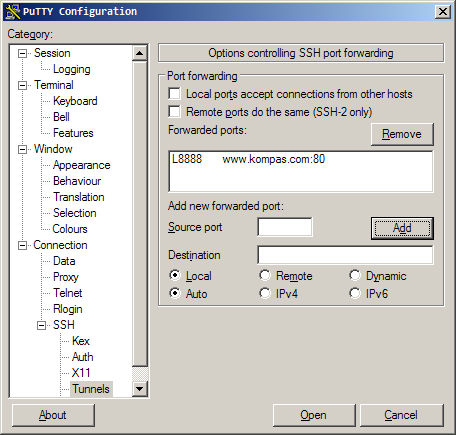
ssh server, maka itu adalah remote port forwarding.ssh -L localport:servertujuan:porttujuan user@ssh_server
ssh -L 8888:www.kompas.com:80 admin@serverku.com
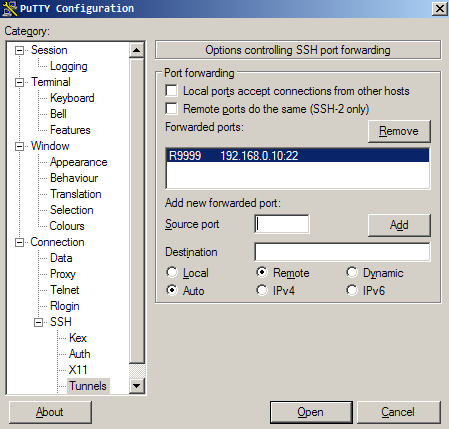
ssh -R remoteport:servertujuan:porttujuan user@ssh_server
ssh -R 8080:192.168.1.1:80 admin@serverku.com

backup: # mysqldump -u root -p[root_password] [database_name] > dumpfilename.sql
restore:# mysql -u root -p[root_password] [database_name] < dumpfilename.sql
# mysqldump -u root -ptmppassword sugarcrm > sugarcrm.sql
# mysqldump -u root -p[root_password] [database_name] > dumpfilename.sql
The sugarcrm.sql will contain drop table, create table and insert
command for all the tables in the sugarcrm database. Following is a
partial output of sugarcrm.sql, showing the dump information of
accounts_contacts table:--
-- Table structure for table `accounts_contacts`
--
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `accounts_contacts`;
SET @saved_cs_client = @@character_set_client;
SET character_set_client = utf8;
CREATE TABLE `accounts_contacts` (
`id` varchar(36) NOT NULL,
`contact_id` varchar(36) default NULL,
`account_id` varchar(36) default NULL,
`date_modified` datetime default NULL,
`deleted` tinyint(1) NOT NULL default '0',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `idx_account_contact` (`account_id`,`contact_id`),
KEY `idx_contid_del_accid` (`contact_id`,`deleted`,`account_id`)
) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
SET character_set_client = @saved_cs_client;
--
-- Dumping data for table `accounts_contacts`
--
LOCK TABLES `accounts_contacts` WRITE;
/*!40000 ALTER TABLE `accounts_contacts` DISABLE KEYS */;
INSERT INTO `accounts_contacts` VALUES ('6ff90374-26d1-5fd8-b844-4873b2e42091',
'11ba0239-c7cf-e87e-e266-4873b218a3f9','503a06a8-0650-6fdd-22ae-4873b245ae53',
'2008-07-23 05:24:30',1),
('83126e77-eeda-f335-dc1b-4873bc805541','7c525b1c-8a11-d803-94a5-4873bc4ff7d2',
'80a6add6-81ed-0266-6db5-4873bc54bfb5','2008-07-23 05:24:30',1),
('4e800b97-c09f-7896-d3d7-48751d81d5ee','f241c222-b91a-d7a9-f355-48751d6bc0f9',
'27060688-1f44-9f10-bdc4-48751db40009','2008-07-23 05:24:30',1),
('c94917ea-3664-8430-e003-487be0817f41','c564b7f3-2923-30b5-4861-487be0f70cb3',
'c71eff65-b76b-cbb0-d31a-487be06e4e0b','2008-07-23 05:24:30',1),
('7dab11e1-64d3-ea6a-c62c-487ce17e4e41','79d6f6e5-50e5-9b2b-034b-487ce1dae5af',
'7b886f23-571b-595b-19dd-487ce1eee867','2008-07-23 05:24:30',1);
/*!40000 ALTER TABLE `accounts_contacts` ENABLE KEYS */;
UNLOCK TABLES;
# mysql -u root -ptmppassword
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| bugs |
| mysql |
| sugarcr |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
For example, if you want to take backup of both sugarcrm and bugs database, execute the mysqldump as shown below:# mysqldump -u root -ptmppassword --databases bugs sugarcrm > bugs_sugarcrm.sql
Verify the bugs_sugarcrm.sql dumpfile contains both the database backup.# grep -i "Current database:" /tmp/bugs_sugarcrm.sql
-- Current Database: `mysql`
-- Current Database: `sugarcrm`
# mysqldump -u root -ptmppassword --all-databases > /tmp/all-database.sql
# mysqldump -u root -ptmppassword sugarcrm accounts_contacts \
> /tmp/sugarcrm_accounts_contacts.sql
# mysql -u root -ptmppassword
mysql> create database sugarcrm;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.02 sec)
# mysql -u root -ptmppassword sugarcrm < /tmp/sugarcrm.sql
# mysql -u root -p[root_password] [database_name] < dumpfilename.sql
[local-server]# mysqldump -u root -ptmppassword sugarcrm | mysql \
-u root -ptmppassword --host=remote-server -C sugarcrm1
[Note: There are two -- (hyphen) in front of host]
If you liked this article, please bookmark it on del.icio.us and Stumble it.