Fault tolerance dalam suati server dapat berupa:
• Redundant Power supply (power supply cadangan)
• Redundant FAN
• Online spare (Memory & HDD)
• Mirroring (Memory & HDD)
• RAID 1, RAID 5, dan RAID 6
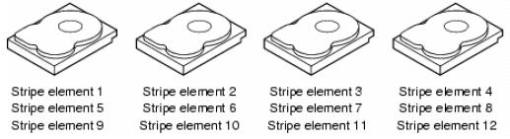
RAID 0 (Disk Striping)
Disk Striping mengijinkan kita untuk menulis data ke beberapa Harddisk daripada menulis data ke satu Harddisk saja. Dengan Disk Striping, setiap Harddisk fisik akan dibagi menjadi beberapa elemen stripe (berkisar antara 8 KB, 16 KB, 32 KB, 64 KB, 128 KB, 256KB, 512KB, to 1024KB). Setiap bagian stripe dalam setiap Harddisk disebut strip.
Disk Striping dapat meningkatkan kinerja karena pengaksesan data diakses dengan lebih dari satu harddisk, sehingga lebih banyak spindle disk yang bekerja dalam melayani I/O data. Namun Disk Striping (RAID 0) tidak memiliki data redundancy / proteksi data terhadap kerusakan harddisk, karena semua data ditulis langsung apa adanya ke semua Harddisk.
Dari sisi kapasitas, maka RAID 0 kita dapat menggunakan 100% dari total jumlah kapasitas harddisk yang terpasang.
Contoh: 4 unit Harddisk 300GB RAID 0 akan menghasilkan total kapasitas yang dapat digunakan sebesar
1.2TB
RAID 1 (Disk Mirroring)
RAID 1 (Disk Mirroring) bekerja dengan prinsip cermin, yaitu berpasang-pasangan dan identik antara satu dengan yang lainnya. Jadi dengan RAID 1, data yang ditulis ke satu Harddisk secara simultan ditulis juga ke Harddisk yang lainnya. Sehingga jika terjadi kerusakan 1 Harddisk pada RAID 1, system server masih memiliki data cadangan di harddisk yang lainnya. Dan pada saat Harddisk yang rusak diganti dengan yang baru, maka secara otomatis, harddisk pengganti yang baru dipasang akan melakukan sinkronisasi data dengan harddisk yang masih berfungsi (rebuilding) Keuntungan dari RAID 1 adalah data memiliki cadangan antara yang ada di harddisk yang satu dengan yang lainnya. Dan karena isi dari kedua Harddisk tersebut adalah identik, tidak jadi masalah harddisk yang mana yang boleh rusak selama pada suatu saat hanya satu Harddisk yang rusak, sampai proses sinkronisasi berikutnya selesai.
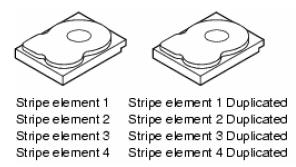
Dari sisi kapasitas, maka RAID 1 kita akan hanya memiliki kapasitas harddisk yang dapat digunakan sebanyak 50% dari total kapasitas Harddisk yang terpasang
Contoh: 4 unit Harddisk 300GB RAID 1 akan menghasilkan total kapasitas yang dapat digunakan sebesar 600GB.
RAID 5 (Disk Striping with Distributed Parity)
Sesuai dengan namaya, cara kerja RAID 5 sama dengan cara kerja RAID 0, yaitu menggunakan disk striping.Yang membedakan anatara keduanya adalah Parity. Parity ini digunakan untuk pengecekan dan perbaikan kesalahan (error checking and correcting). Parity ini disebar di beberapa disk untuk menghindari pengurangan kinerja (Performance bottleneck) pada saat pembuatan parity. Jika Parity disimpan di satu harddisk saja, maka disebut RAID 3 (Disk Striping with Dedicated Parity). Dengan adanya parity ini, maka system RAID 5 tersebut akan tetap berfungsi jika ada salah satu harddisk dalam RAID 5 tersebut itu rusak. Dan harddisk yang rusak tersebut dapat harddisk yang mana saja selama berada dalam satu system RAID 5 yang sama. Karena parity ini berasal dari perhitungan matematik dari suatu beberapa pecahan data, maka, pada saat ada satu bagian pecahan data yang hilang/rusak, system RAID 5 dapat “mengetahui” pecahan data yang hilang tesebut dengan menghitung ulang parity dengan pecahan data yang lainnya.
Secara sederhana, parity bisa dianalogikan dengan perhitungan matematik sbb; 6 + 5 = 11. Dimana angka 6 & 5 adalah data, dan angka 11 adalah parity. Jika suatu saat angka (Harddisk) 5 mengalami kerusakan, maka system dapat menghitung ulang berdasarkan parity (angka 11), angka(Harddisk) apa yang hilang tersebut. Jadi data yang ada pada harddisk yang rusak, tetaplah rusak, hanya saja dengan bantuan parity maka data pada harddisk yang hilang tersebut dapat dihitung ulang kembali. Hal ini juga yang menyebabkan untuk RAID 5 mengalami kerusakan harddisk adalah sebanyak 1 harddisk saja pada suatu saat.Kembali dengan analogi matematik diatas, jika angka (Harddisk) 6 + 5 hilang, maka kemungkinan angka 11 didapat bisa memiliki banyak kemungkinan, seperti 2+9, 3 + 8, dst. komputer tidak dapat membuat suatu perhitungan yang tepat jika data yang tersedia memiliki banyak kemungkinan.
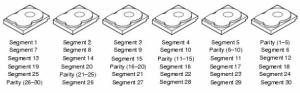
Dari sisi kapasitas, maka RAID 5 kita akan memiliki kapasitas harddisk yang dapat digunakan sebanyak (N-1) x Kapasitas HDD dari total kapasitas Harddisk yang terpasang, dimana N adalah jumlah Harddisk.
Contoh:
• 3 unit Harddisk 300GB RAID 5 akan menghasilkan total kapasitas yang dapat digunakan sebesar 600GB.
• 4 unit Harddisk 300GB RAID 5 akan menghasilkan total kapasitas yang dapat digunakan sebesar 900GB.
• 5 unit Harddisk 300GB RAID 5 akan menghasilkan total kapasitas yang dapat digunakan sebesar 1.2TB, dst.
RAID 6 (Disk Striping with Dual Parity)
(*mulai didukung HANYA di PERC6 dan selanjutnya)
Dapat dilihat dari namanya, RAID 6 menggunakan cara kerja dan konsep yang sama dengan RAID 5 dari sisi penulisan data yang tersebar di beberapa hard disk. Yang membedakan antara RAID 6 dan RAID 5 adalah jumlah parity yang ditulis pada saat penulisan data. Jika RAID 5 menggunakan satu parity, maka RAID 6 menggunakan dua parity. Dengan menulis 2 parity, maka RAID 6 dapat mengakomodasikan kerusakan harddisk maksimal 2 unit pada saat yang bersamaan
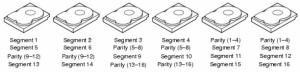
Dari sisi kapasitas, maka RAID 6 kita akan memiliki kapasitas harddisk yang dapat digunakan sebanyak (N-2) x Kapasitas HDD dari total kapasitas Harddisk yang terpasang, dimana N adalah jumlah Harddisk.
Contoh:
• 4 unit Harddisk 300GB RAID 6 akan menghasilkan total kapasitas yang dapat digunakan sebesar 600GB.
• 5 unit Harddisk 300GB RAID 6 akan menghasilkan total kapasitas yang dapat digunakan sebesar 900GB.
• 6 unit Harddisk 300GB RAID 6 akan menghasilkan total kapasitas yang dapat digunakan sebesar 1.2TB, dst.
Sekian pembahasan tentang RAID, semoga bermanfaat.
Source : https://nasari.wordpress.com/2010/04/30/pengertian-raid/